Best-in-class Endpoint Security for Linux
Discover, monitor, and protect linux endpoints before they gets compromised.
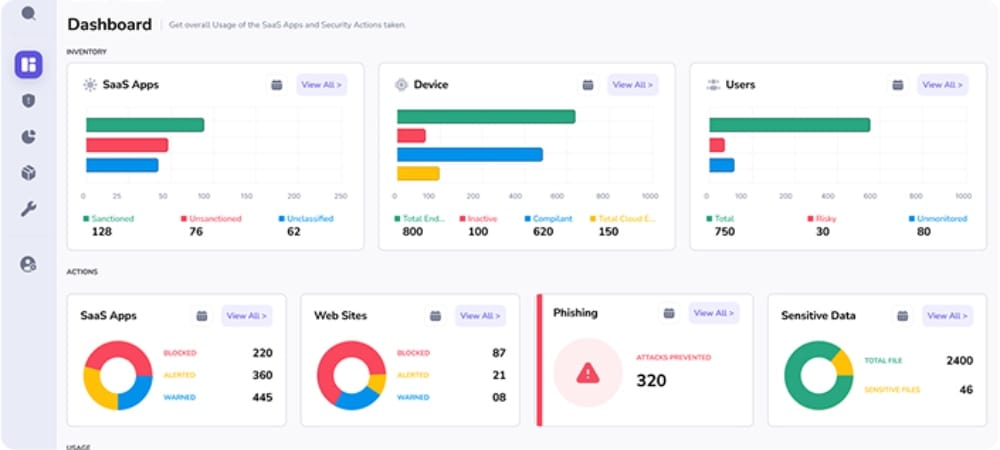
Linux Security
Features Designed for Linux Endpoint Security
Linux devices are increasingly targeted by cybercriminals due to their role in servers and critical IT infrastructure. A single breach can disrupt operations and compromise sensitive data. Kitecyber’s Linux Endpoint Security provides AI-powered, proactive defense to detect and neutralize threats before they cause harm.
Secure Service Edge (SSE)
Provide secure access to the web, SaaS, & private applications.
Linux DLP
Comprehensive Data Loss Prevention tailored for Linux systems.
Anti-phishing Prevention
Protect Linux endpoints against phishing attacks in real-time.
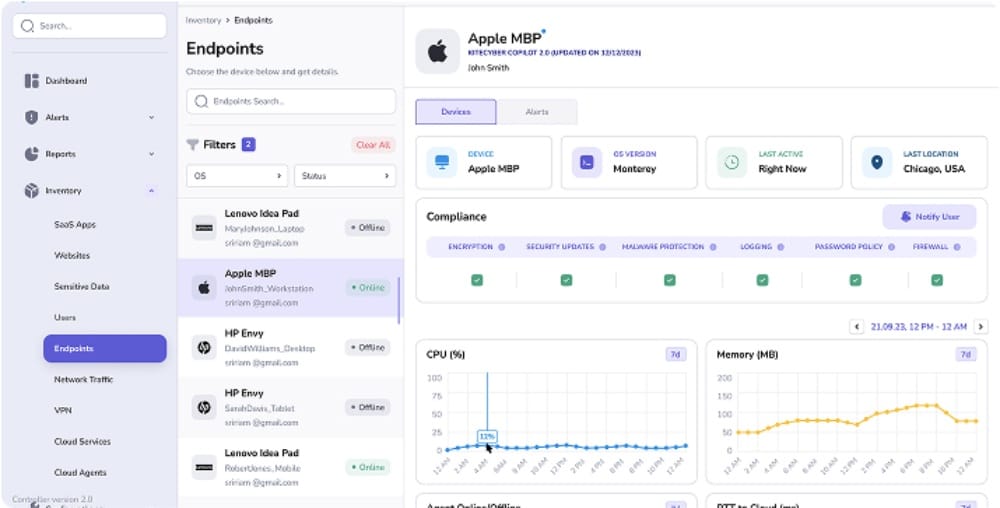
Device Management
Protect linux OS devices by enforcing better access controls.
Global Security Compliance
Supports global security standards like GDPR, SOC 2, and PCI DSS.
Zero Trust VPN
#1 passwordless VPN alternative & replacement for windows.
Linux Isn’t “Immune” to Cyber Attack. It’s a Target.
Most Businesses assume Linux is inherently secure. But built-in
controls aren’t enough when attackers see Linux as a high-value bullseye:
75%
of Linux malware in 2023 exploited outdated software
- (Linux Threat Report)
15%
of ransomware campaigns targeted Linux servers
–Cybersecurity Landscape Report
1000s
of machines infected by stealthy Linux malware
– Wired
Generic security tools fail Linux environments. They lack visibility into kernel-level threats, SSH exploits, and Linux-specific attack paths.
AI-Driven Linux Security
Kitecyber: Smart AI-Powered Endpoint Security for Linux
Omni Channel identity theft protection
What is Linux Endpoint Security?
Linux endpoint security refers to measures and software that protect Linux-based devices and networks from both external and internal threats. These solutions secure endpoints like desktops, laptops, and servers, safeguarding data and ensuring system integrity.
Endpoint security for Linux is your shield against:
External attacks
(malware, ransomware, zero-days)
Insider threats
(misconfigurations, sensitive data leak, credential abuse)
Compliance gaps
(GDPR, SOC 2, PCI DSS)
Linux endpoint security is not just another “antivirus for Linux.” It includes continuous protection like monitoring processes, files, and network activity to stop breaches before data is stolen.
The Hard Truth: Linux Security Challenges
Visibility Gaps
- No kernel-level monitoring for rootkits or LD_PRELOAD hijacking
- Blind spots in cloud workloads (containers, serverless)
Compliance Headaches
- Manual audits for CIS benchmarks, PCI DSS, HIPAA
- No auto-remediation for misconfigurations
Performance Trade-offs
- Legacy security tools slow down critical systems
- Alert fatigue from noisy, non-Linux-specific detections
Advanced Threats
- Fileless attacks living purely in memory
- Credential stuffing via exposed SSH ports
Best Practices for Linux Endpoint Security (And How Kitecyber Automates Them)
| Best Practice | Kitecyber’s Solution |
|---|---|
Patch outdated software | Patch Management Software |
Enforce least privilege | Role-based access control (RBAC) + sudo command monitoring |
Monitor file integrity | Real-time FIM for critical system files (e.g., /etc/passwd) |
Compliance Controls | Security configuration audits for Linux endpoints using certified CIS benchmarks, providing |
Zero Trust Network Access | Passwordless VPN alternative with device + identity checks |
Linux DLP | Sensitive data classification and lineage tracking across linux endpoint + User Behavior Analytics |
AI powered Anti Phishing | Omnichannel phishing prevention with AI, including email, web, SaaS apps, messaging, and desktop |
Device Management | Seamlessly track linux devices, whether managed or unmanaged (BYOD) |
SaaS Security | Secure sanctioned and unsanctioned SaaS apps |
Why Choose Kitecyber for Linux Endpoint Security?
Linux-Specific DLP
Block unauthorized data exfiltration (even via curl or scp).
Secure Web Gateway (SWG)
Filter malicious traffic to SaaS apps, cloud shells, and APIs.
Anti-Phishing Engine
Detect credential theft attempts targeting Linux admins.
Compliance-Ready
Pre-mapped controls for GDPR, SOC 2, PCI DSS.
Lightweight Agent
1.2% CPU, 200 MB RAM usage —no performance drag.
Don’t Let Linux Be Your Weakest Link
The average breach costs $4.45 million — and Linux attacks are rising fastest.
How it works
Frequently asked questions
- Real-time threat detection to identify malware and suspicious activities
- Firewall and network monitoring to prevent unauthorized access
- Behavioral analysisto detect anomalous user or system behavior
- Privilege management to enforce the principle of least privilege
- Automated patching to keep the system updated with the latest security fixes
- Regularly update and patch your system
- Use strong authentication methods, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA)
- Implement firewall rules and restrict unnecessary network access
- Disable unused services and remove unnecessary software
- Enable logging and security monitoring to detect anomalies
- ClamAV – An open-source antivirus for Linux
- SELinux/AppArmor – Access control security frameworks
- Fail2Ban – Protects against brute-force attacks
- OSSEC – Host-based intrusion detection system (HIDS)
- Falco – Runtime security monitoring for Linux containers and cloud environments